|
|
||
  ST-Hadoop is a MapReduce framework that acknowledges the fact that space and time play a crucial role in query processing.
ST-Hadoop is an open-source extension of a Hadoop framework that injects the spatiotemporal awareness in the code base of four layers inside
SpatialHadoop, namely, language, indexing, MapReduce, and operations layers. The spatio-temporal indexing techniques inside ST-Hadoop primarily
tuned to provide the accommodation of new updated dataset efficiently without the need to rebuild its index.
The key point behind the performance gain of ST-Hadoop is the idea of indexing, where data are temporary loaded and divided across
computation nodes.
For more information, please visit: "http://st-hadoop.cs.umn.edu/"
ST-Hadoop is a MapReduce framework that acknowledges the fact that space and time play a crucial role in query processing.
ST-Hadoop is an open-source extension of a Hadoop framework that injects the spatiotemporal awareness in the code base of four layers inside
SpatialHadoop, namely, language, indexing, MapReduce, and operations layers. The spatio-temporal indexing techniques inside ST-Hadoop primarily
tuned to provide the accommodation of new updated dataset efficiently without the need to rebuild its index.
The key point behind the performance gain of ST-Hadoop is the idea of indexing, where data are temporary loaded and divided across
computation nodes.
For more information, please visit: "http://st-hadoop.cs.umn.edu/"
|
||
|
|
||
 Kite is an open-source system to index and query Twitter-like data (Microblogs data).
Microblogs in general are the micro-length posts that are generated by hundreds of millions of web users everyday,
like tweets, online reviews for products and movies, user comments on news media or social media, and user check-ins on location-aware web
services. This data is easy-to-produce by users and so it comes literally in thousands of records every single second, carrying very rich
user-generated contents such as news, opinions, discussions, as well as meta data including location information, language information,
and personal information. The rich content and the popularity of microblogging platforms results in Microblogs being exploited in a wide
variety of important applications including disseminating news and citizen journalism, events detection and analysis, rescue services during
natural disasters, and geo-targeted advertising. Kite provides the scalable infrastructure to query this data efficiently without worrying
about all the complications of managing the data under the hood. Using Kite, one can build a very efficient application on top of Microblogs in
just few minutes. Kite is implemented as a distributed system on top of Apache Ignite system and Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS).
It is scalable to digest more than 10,000 Microblog/second on each machine with tunable memory resources usage. It could organize billions
of historical data in efficient temporal index structures to be queried very fast. Kite also provides real-time query response in the order of
few milliseconds for a variety of queries on spatial and non-spatial attributes. For more information,
pleease visit: "http://kite.cs.umn.edu/"
Kite is an open-source system to index and query Twitter-like data (Microblogs data).
Microblogs in general are the micro-length posts that are generated by hundreds of millions of web users everyday,
like tweets, online reviews for products and movies, user comments on news media or social media, and user check-ins on location-aware web
services. This data is easy-to-produce by users and so it comes literally in thousands of records every single second, carrying very rich
user-generated contents such as news, opinions, discussions, as well as meta data including location information, language information,
and personal information. The rich content and the popularity of microblogging platforms results in Microblogs being exploited in a wide
variety of important applications including disseminating news and citizen journalism, events detection and analysis, rescue services during
natural disasters, and geo-targeted advertising. Kite provides the scalable infrastructure to query this data efficiently without worrying
about all the complications of managing the data under the hood. Using Kite, one can build a very efficient application on top of Microblogs in
just few minutes. Kite is implemented as a distributed system on top of Apache Ignite system and Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS).
It is scalable to digest more than 10,000 Microblog/second on each machine with tunable memory resources usage. It could organize billions
of historical data in efficient temporal index structures to be queried very fast. Kite also provides real-time query response in the order of
few milliseconds for a variety of queries on spatial and non-spatial attributes. For more information,
pleease visit: "http://kite.cs.umn.edu/"
|
||
|
|
||
  SpatialHadoop
is an open source MapReduce framework with built-in
support for spatial data. It employs the MapReduce programming paradigm
for distributed processing to build a general purpose tool for large
scale analysis of spatial data on large clusters. Users can interact
easily with SpatialHadoop through a high level language with built-in
support for spatial data types and spatial operations. Existing spatial
data sets can be loaded in SpatialHadoop with the built in spatial data
types point, polygon and rectangle. SpatialHadoop is also extensible
and more data types can be added by users. In addition, the data sets
are stored efficiently using built-in indexes (Grid file or R-tree)
which speed up the retrieval and processing of these data sets. Users
can build an index of their choice with a single command that runs in
parallel on the machines in the cluster. Once the index is built, users
can start analyzing their data sets using the built in spatial
operations (range query, k nearest neighbor and spatial join). The
extensibility of SpatialHadoop allows users to implement more spatial
operations as MapReduce programs. For more information, please visit: "http://spatialhadoop.cs.umn.edu/" SpatialHadoop
is an open source MapReduce framework with built-in
support for spatial data. It employs the MapReduce programming paradigm
for distributed processing to build a general purpose tool for large
scale analysis of spatial data on large clusters. Users can interact
easily with SpatialHadoop through a high level language with built-in
support for spatial data types and spatial operations. Existing spatial
data sets can be loaded in SpatialHadoop with the built in spatial data
types point, polygon and rectangle. SpatialHadoop is also extensible
and more data types can be added by users. In addition, the data sets
are stored efficiently using built-in indexes (Grid file or R-tree)
which speed up the retrieval and processing of these data sets. Users
can build an index of their choice with a single command that runs in
parallel on the machines in the cluster. Once the index is built, users
can start analyzing their data sets using the built in spatial
operations (range query, k nearest neighbor and spatial join). The
extensibility of SpatialHadoop allows users to implement more spatial
operations as MapReduce programs. For more information, please visit: "http://spatialhadoop.cs.umn.edu/"
|
||
|
|
||
  |
||
|
|
||
  RecDB
is an open source recommendation engine built entirely inside
PostgreSQL 9.2. RecDB allows application developers to build
recommendation applications in a heartbeat through a wide variety of
built-in recommendation algorithms like user-user collaborative
filtering, item-item collaborative filtering, singular value
decomposition. Applications powered by RecDB can produce online and
flexible personalized recommendations to end-users. An out-of-the-box
tool for web and mobile developers to implement a myriad of
recommendation applications. The system is easily used and configured
so that a novice developer can define a variety of recommenders that
fits the application needs in few lines of SQL. Crafted inside
PostgreSQL database engine, RecDB is able to seamlessly integrate the
recommendation functionality with traditional database operations,
i.e., SELECT, PROJECT, JOIN, in the query pipeline to execute ad-hoc
recommendation queries. The system optimizes incoming recommendation
queries (written in SQL) and hence provides near real-time personalized
recommendation to a high number of end-users who expressed their
opionions over a large pool of items. For more information, please
visit: "http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~sarwat/RecDB/" RecDB
is an open source recommendation engine built entirely inside
PostgreSQL 9.2. RecDB allows application developers to build
recommendation applications in a heartbeat through a wide variety of
built-in recommendation algorithms like user-user collaborative
filtering, item-item collaborative filtering, singular value
decomposition. Applications powered by RecDB can produce online and
flexible personalized recommendations to end-users. An out-of-the-box
tool for web and mobile developers to implement a myriad of
recommendation applications. The system is easily used and configured
so that a novice developer can define a variety of recommenders that
fits the application needs in few lines of SQL. Crafted inside
PostgreSQL database engine, RecDB is able to seamlessly integrate the
recommendation functionality with traditional database operations,
i.e., SELECT, PROJECT, JOIN, in the query pipeline to execute ad-hoc
recommendation queries. The system optimizes incoming recommendation
queries (written in SQL) and hence provides near real-time personalized
recommendation to a high number of end-users who expressed their
opionions over a large pool of items. For more information, please
visit: "http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~sarwat/RecDB/"
|
||
|
|
||
  |
||
 Monitoring
personal locations with a potentially untrusted server poses
privacy threats to the monitored individuals. To this end, we propose a
privacy-preserving location monitoring system for wireless sensor
networks. In our system, we design two in-network location
anonymization algorithms, namely, resource- and quality-aware
algorithms, that aim to enable the system to provide high quality
location monitoring services for system users, while preserving
personal location privacy. Both algorithms rely on the well established
k-anonymity privacy concept to enable trusted sensor nodes to provide
the aggregate location information of monitored persons for our system.
Each aggregate location is in a form of a monitored area A along with
the number of monitored persons residing in A, where A contains at
least k persons. The resource-aware algorithm aims to minimize
communication and computational cost, while the quality-aware algorithm
aims to maximize the accuracy of the aggregate locations by minimizing
their monitored areas. To utilize the aggregate location information to
provide location monitoring services, we use a spatial histogram
approach that estimates the distribution of the monitored persons based
on the gathered aggregate location information. The estimated
distribution is used to provide location monitoring services through
answering range queries.
Monitoring
personal locations with a potentially untrusted server poses
privacy threats to the monitored individuals. To this end, we propose a
privacy-preserving location monitoring system for wireless sensor
networks. In our system, we design two in-network location
anonymization algorithms, namely, resource- and quality-aware
algorithms, that aim to enable the system to provide high quality
location monitoring services for system users, while preserving
personal location privacy. Both algorithms rely on the well established
k-anonymity privacy concept to enable trusted sensor nodes to provide
the aggregate location information of monitored persons for our system.
Each aggregate location is in a form of a monitored area A along with
the number of monitored persons residing in A, where A contains at
least k persons. The resource-aware algorithm aims to minimize
communication and computational cost, while the quality-aware algorithm
aims to maximize the accuracy of the aggregate locations by minimizing
their monitored areas. To utilize the aggregate location information to
provide location monitoring services, we use a spatial histogram
approach that estimates the distribution of the monitored persons based
on the gathered aggregate location information. The estimated
distribution is used to provide location monitoring services through
answering range queries. |
|
||
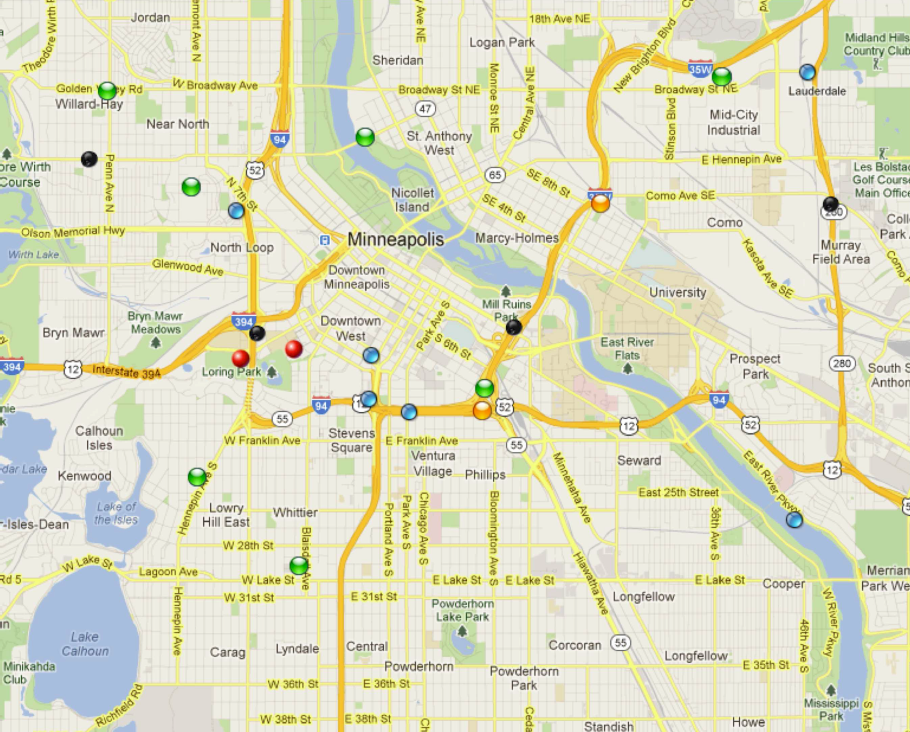
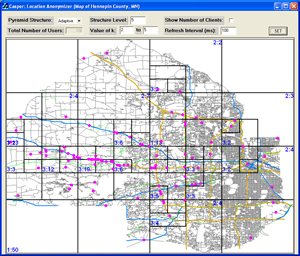  This
project tackles a major privacy concern in current location-based
services where users have to continuously report their locations to the
database server in order to obtain the service. For example, a user
asking about the nearest gas station has to report her exact location.
With untrusted servers, reporting the location information may lead to
several privacy threats. In this paper, we present Casper1; a new
framework in which mobile and stationary users can entertain
location-based services without revealing their location information.
Casper consists of two main components, the location anonymizer and the
privacy-aware query processor. The location anonymizer blurs the users?
exact location information into cloaked spatial regions based on
user-specified privacy requirements. The privacy-aware query processor
is embedded inside the location-based database server in order to deal
with the cloaked spatial areas rather than the exact location
information. This
project tackles a major privacy concern in current location-based
services where users have to continuously report their locations to the
database server in order to obtain the service. For example, a user
asking about the nearest gas station has to report her exact location.
With untrusted servers, reporting the location information may lead to
several privacy threats. In this paper, we present Casper1; a new
framework in which mobile and stationary users can entertain
location-based services without revealing their location information.
Casper consists of two main components, the location anonymizer and the
privacy-aware query processor. The location anonymizer blurs the users?
exact location information into cloaked spatial regions based on
user-specified privacy requirements. The privacy-aware query processor
is embedded inside the location-based database server in order to deal
with the cloaked spatial areas rather than the exact location
information. |
||